rg or fd (#156)
* feat: read workspace files by external commands * fix: avoid errors when it manages invalid buffers * feat: add workspace_scan_cmd to select a way * docs: describe `workspace_scan_cmd` option
telescope-frecency.nvim
A telescope.nvim extension that offers intelligent prioritization when selecting files from your editing history.
Using an implementation of Mozilla's Frecency algorithm (used in Firefox's address bar), files edited frecently are given higher precedence in the list index.
As the extension learns your editing habits over time, the sorting of the list is dynamically altered to prioritize the files you're likely to need.
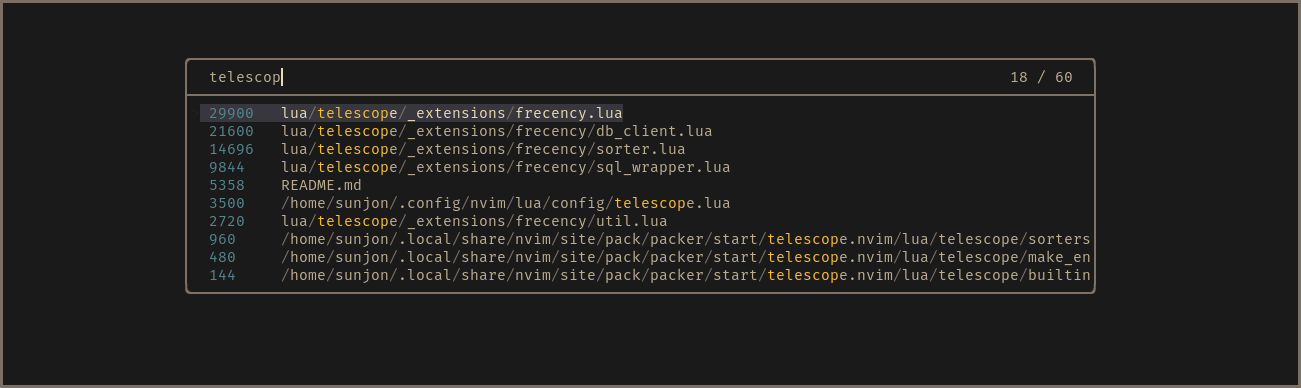
- Scores shown in finder for demonstration purposes - disabled by default
Frecency: Sorting by 'frequency' and 'recency'
'Frecency' is a score given to each unique file indexed in a file history database.
A timestamp is recorded once per session when a file is first loaded into a buffer.
The score is calculated using the age of the 10 (customizable) most recent timestamps and the total amount of times that the file has been loaded:
Recency values (per timestamp)
| Timestamp age | Value |
|---|---|
| 4 hours | 100 |
| 1 day | 80 |
| 3 days | 60 |
| 1 week | 40 |
| 1 month | 20 |
| 90 days | 10 |
Score calculation
score = frequency * recency_score / max_number_of_timestamps
What about files that are neither 'frequent' or 'recent' ?
Frecency naturally works best for indexed files that have been given a reasonably high score.
New projects or rarely used files with generic names either don't get listed at all or can be buried under results with a higher score.
Frecency tackles this with Workspace Filters:

The workspace filter feature enables you to select from user defined filter
tags that map to a directory or collection of directories. Filters are applied
by entering :workspace_tag: anywhere in the query. Filter name completion is
available by pressing <Tab> after the first : character.
When a filter is applied, results are reduced to entries whose path is a descendant of the workspace directory. The indexed results are optionally augmented with a listing of all files found in a recurssive search of the workspace directory. Non-indexed files are given a score of zero and appear below the 'frecent' entries. When a non-indexed file is opened, it gains a score value and is available in future 'frecent' search results.
If the active buffer (prior to the finder being launched) is attached to an LSP
server, an automatic LSP tag is available, which maps to the workspace
directories provided by the language server.
Requirements
- telescope.nvim (required)
- nvim-web-devicons (optional)
- ripgrep or fd (optional)
NOTE: The former version of this plugin has used SQLite3 database to store timestamps and file records. But the current build uses Lua native code to store them, so you can now remove sqlite.lua from dependencies. See Remove dependency for sqlite.lua for the detail.
NOTE: ripgrep or fd will be used to list up workspace files. They are
extremely faster than the native Lua logic. If you don't have them, it
fallbacks to Lua code automatically. See the detail for workspace_scan_cmd
option.
Installation
Packer.nvim
use {
"nvim-telescope/telescope-frecency.nvim",
config = function()
require("telescope").load_extension "frecency"
end,
}
Lazy.nvim
{
"nvim-telescope/telescope-frecency.nvim",
config = function()
require("telescope").load_extension "frecency"
end,
}
If no database is found when running Neovim with the plugin installed, a new
one is created and entries from shada v:oldfiles are automatically
imported.
Usage
:Telescope frecency
or to map to a key:
vim.keymap.set("n", "<leader><leader>", "<Cmd>Telescope frecency<CR>")
Use a specific workspace tag:
:Telescope frecency workspace=CWD
or
vim.keymap.set("n", "<leader><leader>", "<Cmd>Telescope frecency workspace=CWD<CR>")
Filter tags are applied by typing the :tag: name (adding surrounding colons)
in the finder query. Entering :<Tab> will trigger omnicompletion for
available tags.
Configuration
See default configuration for full details on configuring Telescope.
-
db_root(default:vim.fn.stdpath "data")Path to parent directory of custom database location. Defaults to
$XDG_DATA_HOME/nvimif unset. -
default_workspace(default:nil)Default workspace tag to filter by e.g.
'CWD'to filter by default to the current directory. Can be overridden at query time by specifying another filter like':*:'. -
disable_devicons(default:false)Disable devicons (if available)
-
ignore_patterns(default:{ "*.git/*", "*/tmp/*", "term://*" })Patterns in this table control which files are indexed (and subsequently which you'll see in the finder results).
-
max_timestamps(default:10)Set the max count of timestamps DB keeps when you open files. It ignores the value and use
10if you set less than or equal to0.CAUTION When you reduce the value of this option, it removes old timestamps when you open the file. It is reasonable to set this value more than or equal to the default value:
10. -
show_filter_column(default:true)Show the path of the active filter before file paths. In default, it uses the tail of paths for
'LSP'and'CWD'tags. You can configure this by setting a table for this option.-- show the tail for "LSP", "CWD" and "FOO" show_filter_column = { "LSP", "CWD", "FOO" } -
show_scores(default :false)To see the scores generated by the algorithm in the results, set this to
true. -
show_unindexed(default:true)Determines if non-indexed files are included in workspace filter results.
-
use_sqlite(default:false)Use sqlite.lua with
trueor native code withfalse. See Remove dependency for sqlite.lua for the detail. -
workspace_scan_cmd(default:nil)This option can be set values as
"LUA"|string[]|nil. With the default value:nil, it uses these way below to make entries for workspace files. It tries in order until it works successfully.rg -0.g '!.git' --filesfdfind -0Htffd -0Htf- Native Lua code (old way)
If you like another commands, set them to this option, like
workspace_scan_cmd = { "find", ".", "-type", "f", "-print0" }. This command must use NUL characters for delimiters.If you prefer Native Lua code, set
workspace_scan_cmd = "LUA". -
workspaces(default:{})This table contains mappings of
workspace_tag->workspace_directory. The key corresponds to the:tag_nameused to select the filter in queries. The value corresponds to the top level directory by which results will be filtered.
Example Configuration:
telescope.setup {
extensions = {
frecency = {
db_root = "/home/my_username/path/to/db_root",
show_scores = false,
show_unindexed = true,
ignore_patterns = { "*.git/*", "*/tmp/*" },
disable_devicons = false,
workspaces = {
["conf"] = "/home/my_username/.config",
["data"] = "/home/my_username/.local/share",
["project"] = "/home/my_username/projects",
["wiki"] = "/home/my_username/wiki"
}
}
},
}
Note for Database
Location
The default location for the database is $XDG_DATA_HOME/nvim (eg
~/.local/share/nvim/ on linux). This can be configured with the db_root
config option.
Maintainance
By default, frecency will prune files that no longer exist from the database. In certain workflows, switching branches in a repository, that behaviour might not be desired. The following configuration control this behaviour:
db_safe_mode- When this is enabled, the user will be prompted before any entries are removed from the database.
auto_validate- When this to false, stale entries will never be automatically removed.
The command FrecencyValidate can be used to clean the database when
auto_validate is disabled.
" clean DB
:FrecencyValidate
" clean DB without prompts to confirm
:FrecencyValidate!
Delete entries
You can delete entries from DB by FrecencyDelete command. This command does
not remove the file itself, only from DB.
" delete the current opened file
:FrecencyDelete
" delete the supplied path
:FrecencyDelete /full/path/to/the/file
Remove dependency for sqlite.lua
The former version of this plugin has used SQLite3 library to store data. When
you upgrade from such version, Neovim will silently migrate DB and inform that
you can remove sqlite.lua from dependencies.
| made by default | made by sqlite.lua |
|---|---|
~/.local/share/nvim/file_frecency.bin |
~/.local/share/nvim/file_frecency.sqlite3 |
The DB file will be migrated into a filename above, and old file (SQLite3
version) will still remain. If you still want to use SQLite3 version, set
use_sqlite = true.
Also you can explicitly migrate DB by calling :FrecencyMigrateDB command.
Highlight Groups
TelescopeBufferLoaded
TelescopePathSeparator
TelescopeFrecencyScores
TelescopeQueryFilter
TODO: describe highlight groups